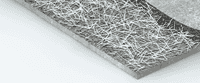
Fibers-reinforced Concrete
Fiber-reinforced (FRC) concrete contains fibrous mono-filament or fibrillated materials, which strengthen concrete structures. These usually consist of polypropylene fibers distinguished into two types according to EN 14889-2: microfibers and macro fibers. The fiber types primarily differ in length and diameter, but more importantly in the function performed in concrete. The length of macro-fibers is usually between 30 and 50 mm. They replace reinforcements in steel bars, by increasing flexural strength, and improving the impact resistance and tensile strength of the concrete. Micro-fibers are generally shorter than 30 mm. They are an alternative to crack control mesh used to enhance concrete durability by overcoming plastic shrinkages, reducing plastic settlement, reducing bleeding, and limiting the formation of cracks.
Polypropylene fibers have an influence on the physical and mechanical properties of concrete such as workability, elasticity modulus, compressive flexural and tensile strength, toughness, impact, spalling, freeze-thaw, abrasion resistance, water absorption, porosity, permeability, durability, and eco-friendly and economic properties of concrete.
Typical applications include slabs, runways, and roads, sprayed concrete, precast concrete, plaster render and stucco, and screeds and overlays.
Holderchem provides technical assistance pertaining to concrete mix designs and offers products required for the production of shrinkage-reduced concrete. It provides guidance with respect to the selection of concrete fibers and their impact on concrete mechanical and physical properties.